The Relative Vigor Index (RVI) was created by John Ehlers, a technical analyst and president of MESA Software, which provides algorithmic trading strategies.
The RVI allows getting buy and sell signals and, due to its versatility, can be included in any trading system.
What is the Relative Vigor Index?
The RVI is more of an oscillator because the movement of this indicator is like a pendulum swinging from one extreme position to another.
The RVI is similar to the Momentum, Accumulation/Distribution, and MACD indicators.
The RVI helps find the exact moment to open the deals and warn in advance about the impending change of the trend with the help of divergence with the price chart.
In our opinion, the RVI should be in the toolkit of any active trader.
How to Calculate the Relative Vigor Index?
The relative vigor index is calculated using the following formula:
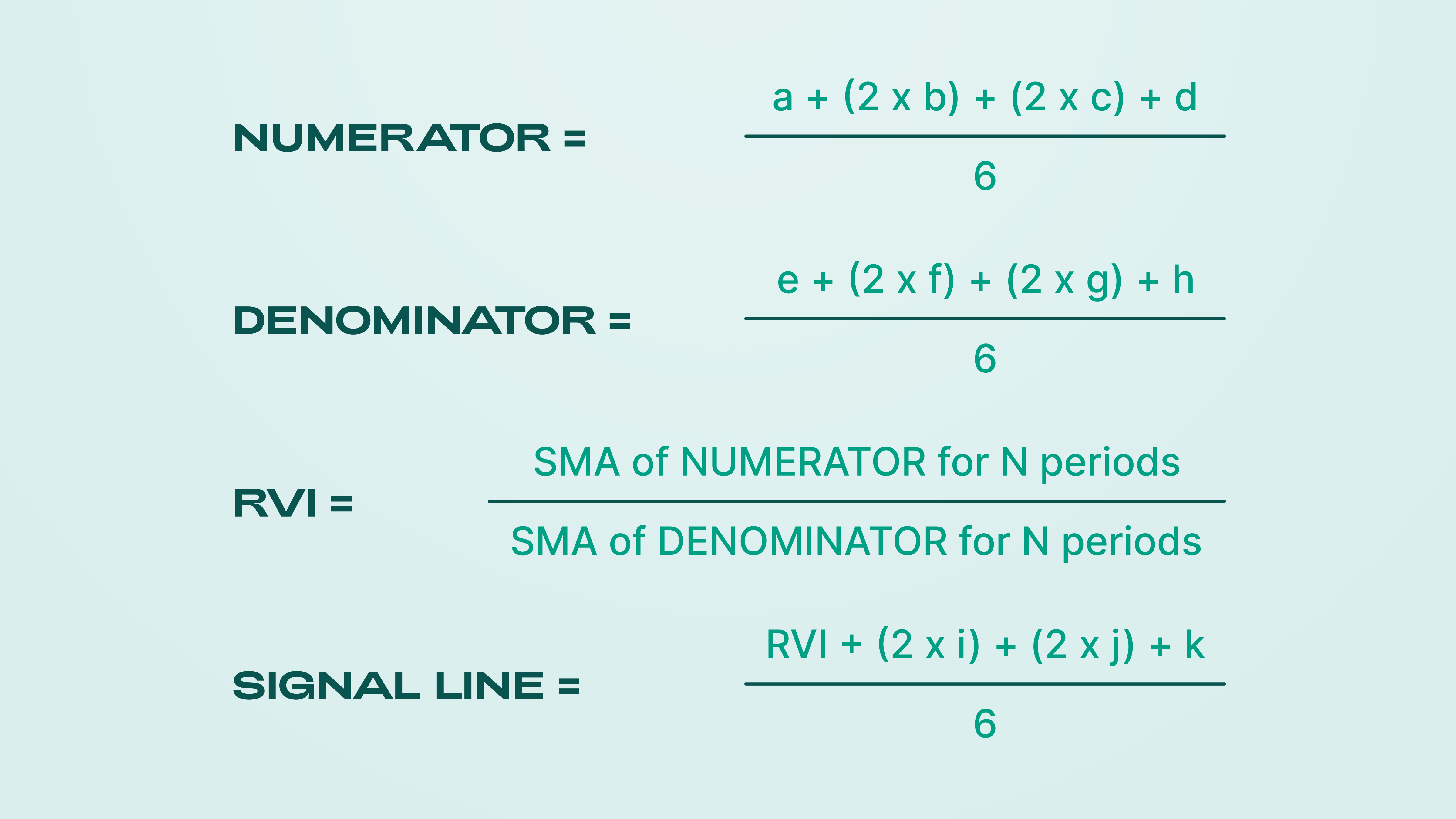
Despite the complexity of the RVI formula, the indicator is quite simple to calculate and use. As you may have noticed, the indicator consists of two lines - the RVI indicator line and the RVI signal line.
Thus it resembles the MACD indicator. By the way, the signals generated by the indicator are also similar to those generated by the MACD indicator from Gerald Appel.
By default, the RVI indicator settings can be left equal to the period set in Metatrader, namely, 10.
How to implement RVI in MetaTrader?
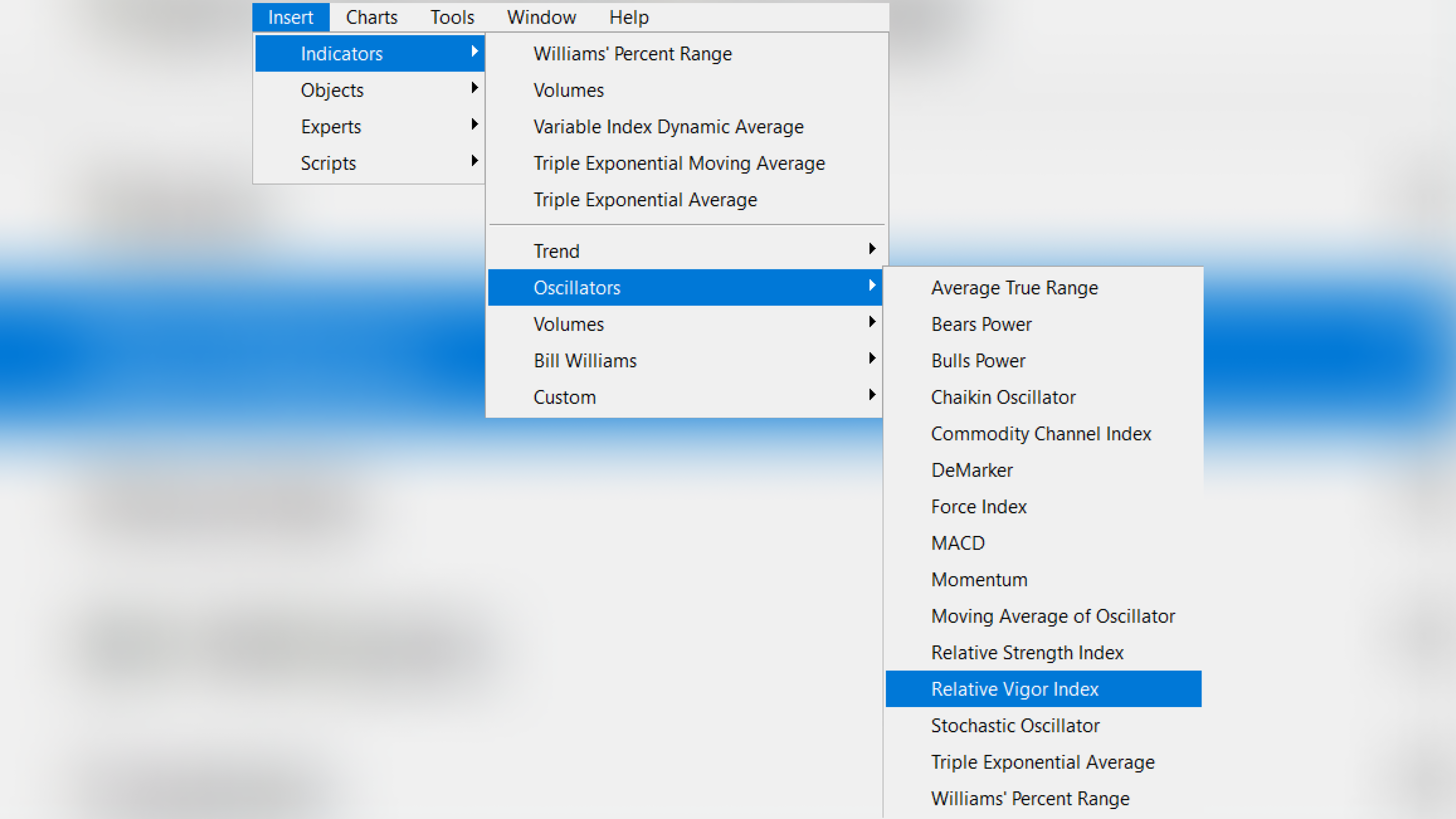
To choose the Relative Vigor Index indicator in MetaTrader 5, it is necessary to select the following:
Insert -> Indicators -> Oscillators -> Relative Vigor Index
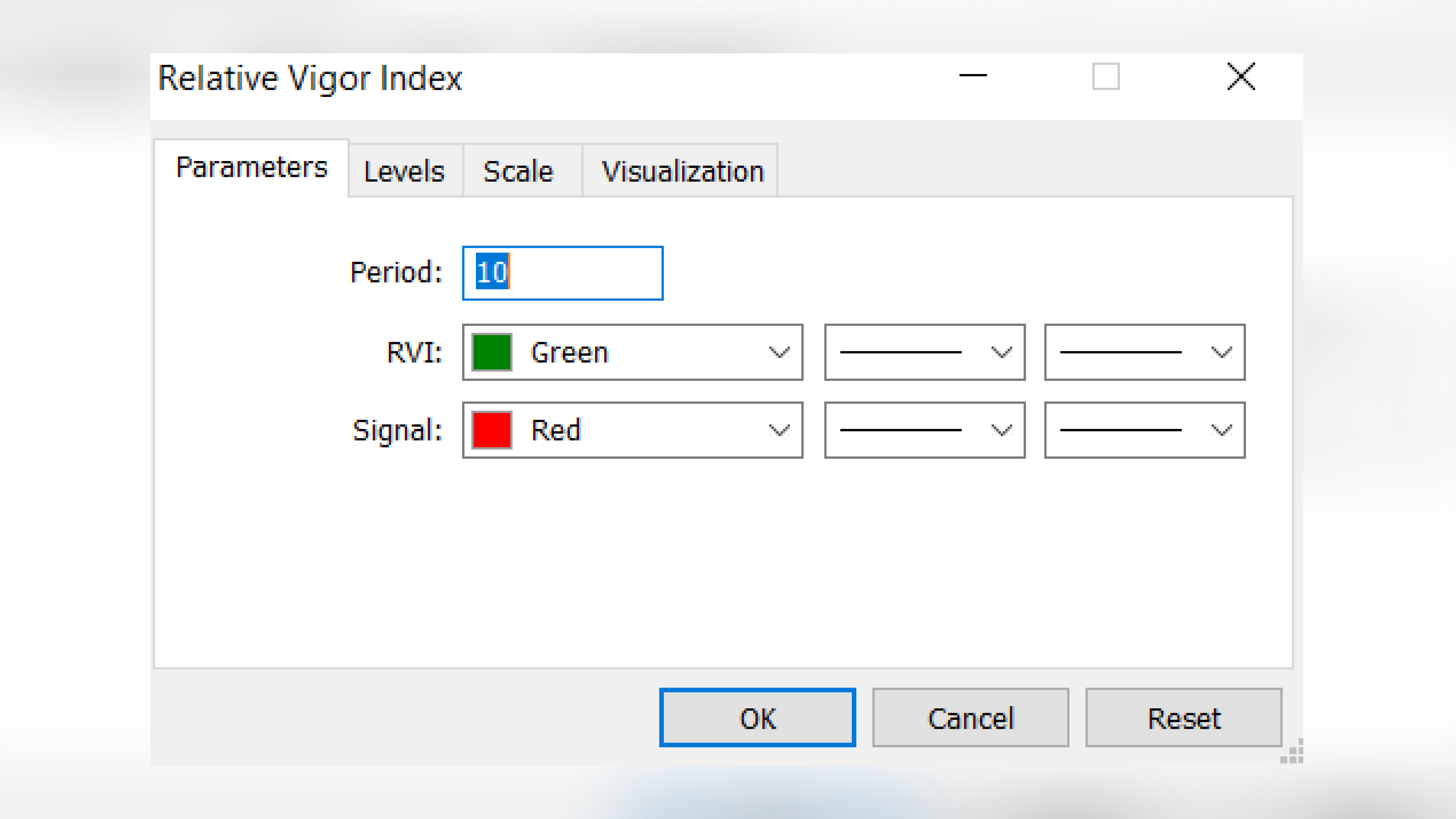
As we already know, the indicator consists of two lines – the RVI line, which is colored green by default in MetaTrader, and the Signal line, which is colored red by default.
The order of the RVI indicator is 10.
How to interpret the RVI Indicator?
Intersection of lines
The first and most important signal from the indicator is the crossing of lines.
When the RVI indicator line crosses the signal line downwards - an RVI trading signal to open a trade downwards is given.
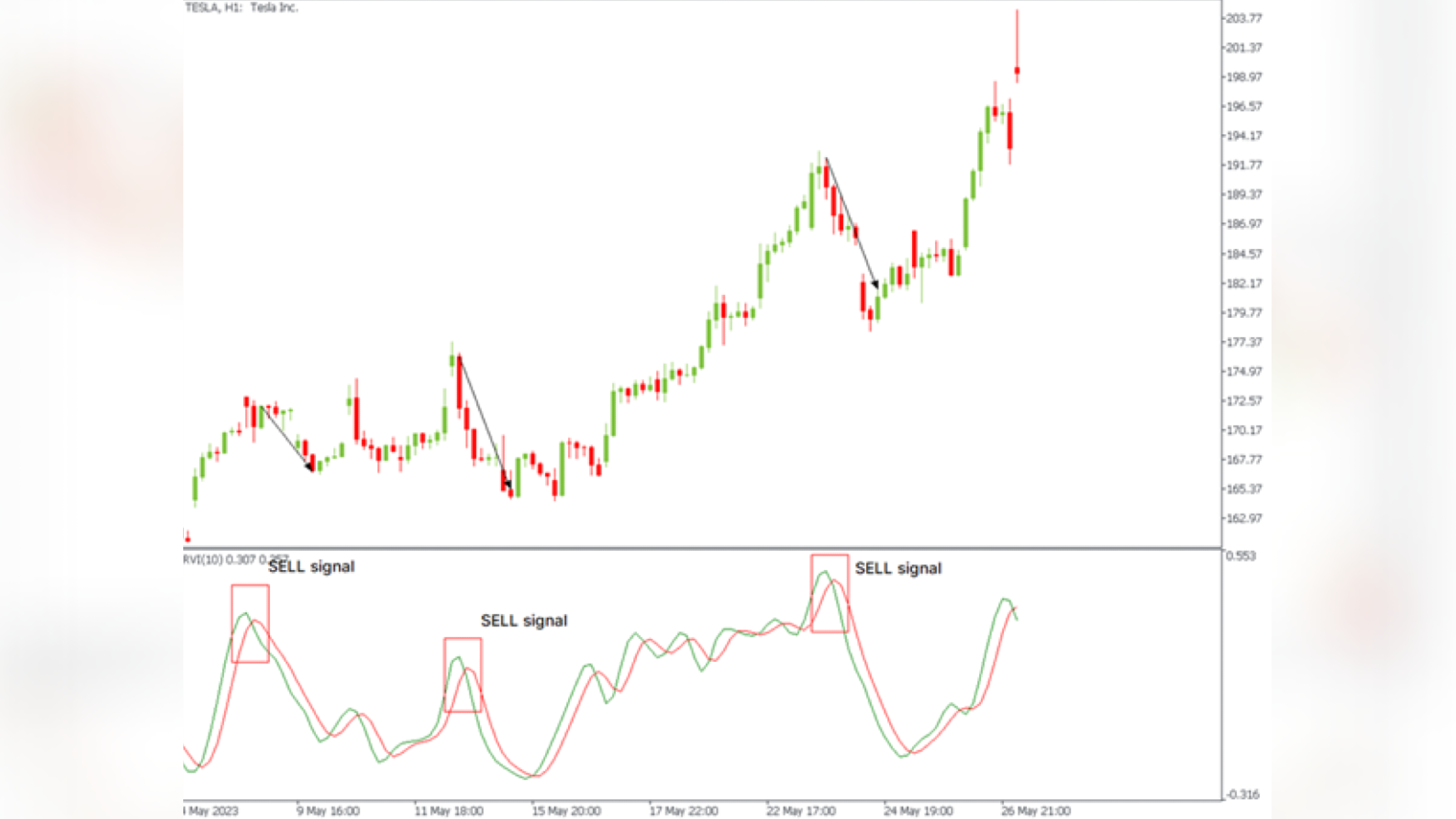
When the RVI indicator line crosses the signal line upwards - a signal to open a trade upwards is given.
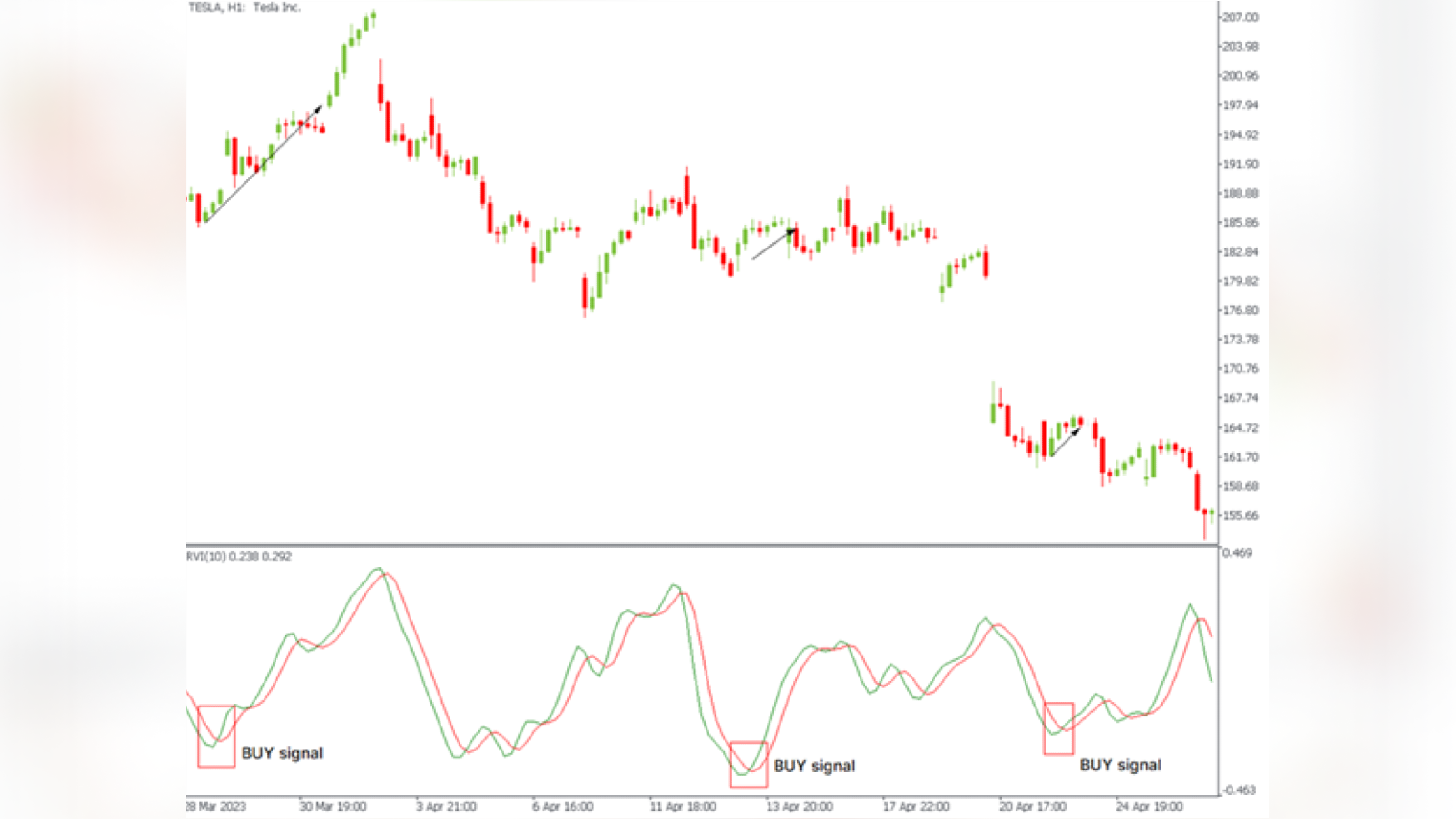
As you can see, in both cases, the indicator gives a lot of false signals. You can use additional indicators to remove false signals, such as the trend Parabolic SAR.
The general setup is as follows: if the RVI gives a buy signal, but the Parabolic SAR is going down, the trade will not be opened. Also, a trade is not opened if the RVI gives a sell signal and the Parabolic SAR increases.
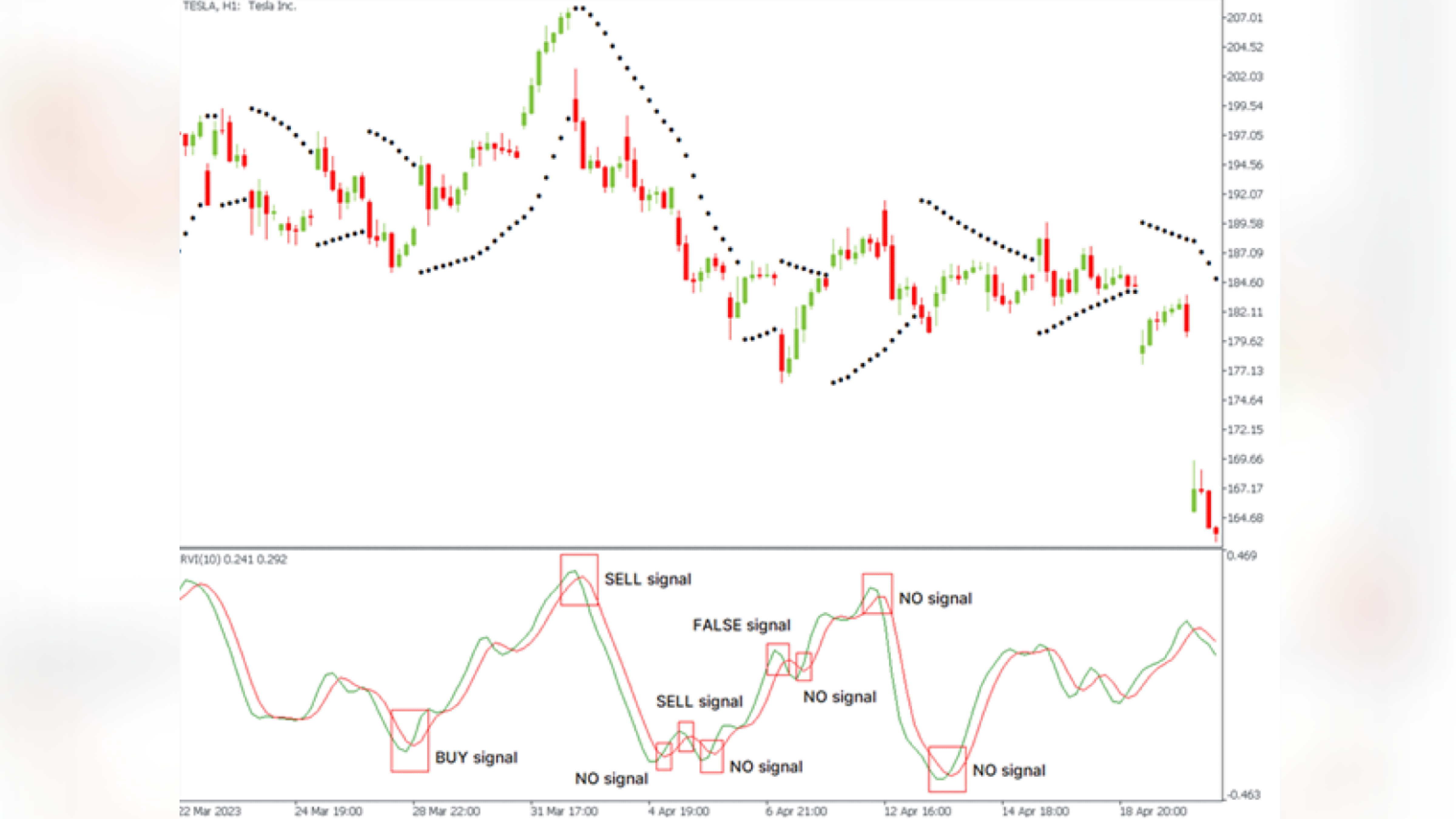
As you can see, some of the false signals are cut off. In the selected area appears only one false signal; however, such a system cuts off also the last two good signals that could bring profit.
Thus, using a combination of certain indicators, the trader sacrifices a few good signals to reduce the risks of the trading system.
Divergence
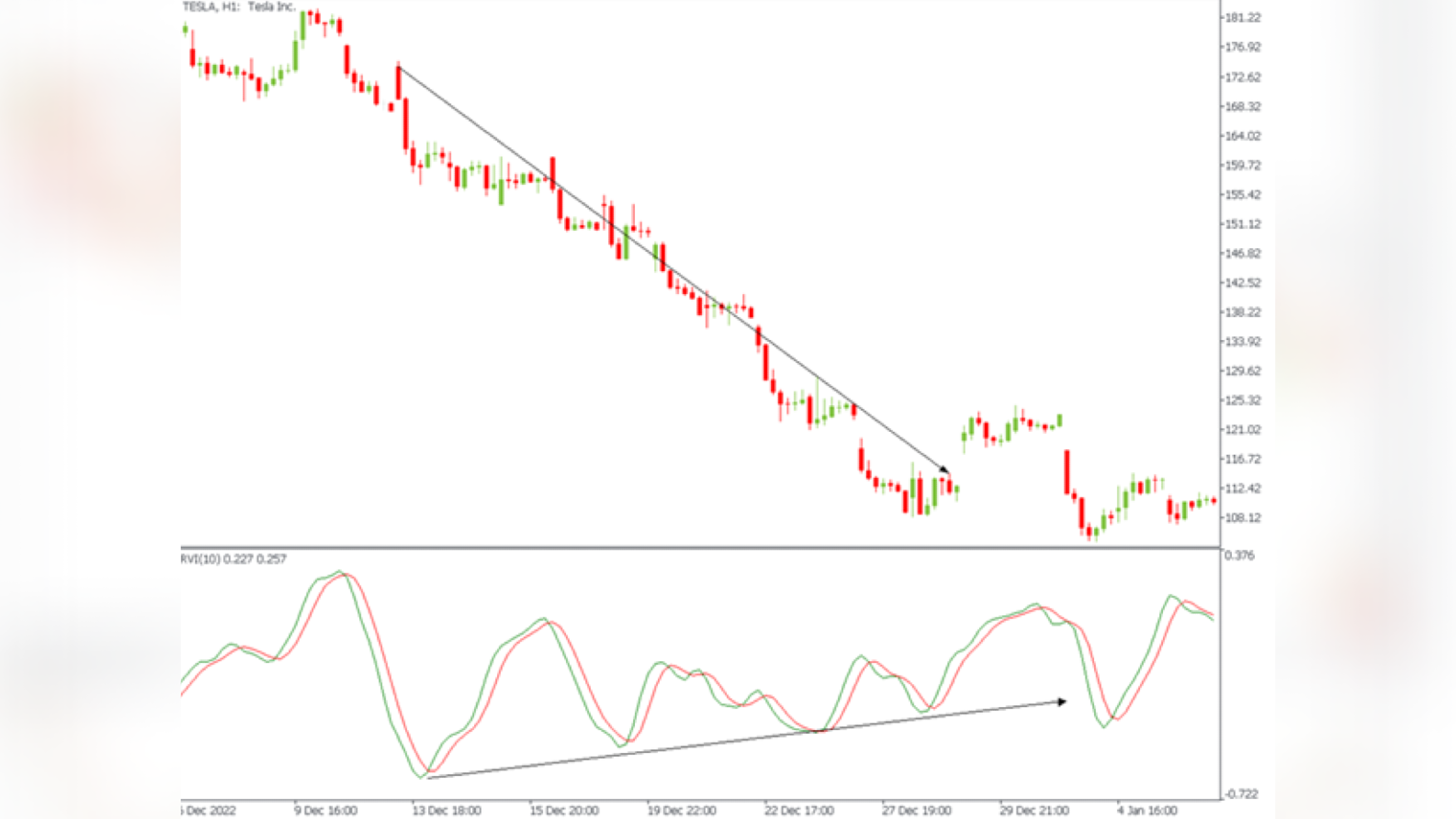
The second signal, which gives the indicator, is less obvious but can also be used in trading - a divergence between the indicator movement and the price chart.
For example, if the indicator rises while the price falls - it indicates a possible imminent price reversal.
This is not a clear signal. However, it only hints at a change in the trend.
Limitations of Using the Relative Vigor Index
RVI cannot be used during a flat market.
Try to use the RVI only when the market is trending.
Conclusion
- RVI is a reasonably effective indicator developed by John Ehlers
- The indicator gives several signals at once - crossing lines and divergence with the price.
- RVI is not used during a flat market.








No comments:
Post a Comment